The fight against inequality was at the heart of the discussions at the G7 Summit that took place in Biarritz, France from 24-26 August 2019. A highlight of the summit, that brought together the heads of governments of the G7 countries as well as the presidents of five African states, was the unanimous confirmation of support and adoption of the G7 Framework on decent job creation for rural youth in the Sahel by the G7 member states. The framework focuses on sustainable food systems and territorial approaches as new inclusive paradigms. It calls for two focus areas, opportunity and capability, to create decent jobs for rural youth in the G5 Sahel countries.
Links

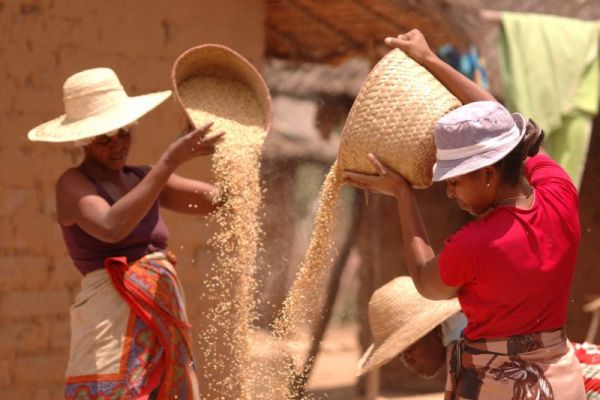
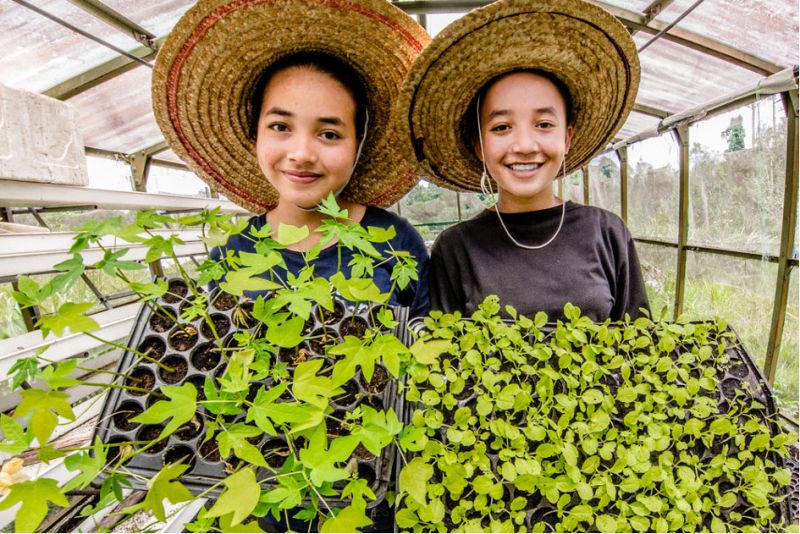
Experts expect the labour force in the Sahel region to increase by 46 million young people (15-35 years old) by 2050, and sustainable food systems will remain a major provider of jobs. Within this framework the G7 will increase their efforts to support decent jobs creation for the rural youth in the Sahel region and will concentrate their efforts on leveraging sustainable food system for decent job creation through all upstream (pre-harvest) and downstream activities including production at farm level, processing, packaging, transportation, distribution and retail, as well as the educational and teaching aspects. The G7 framework also identifies coordination and alignment with G5 Sahel countries’ policies as overarching principles of their partnership.
SUSTAINABLE FOOD SYSTEMS AS A NEW INCLUSIVE PARADIGMS
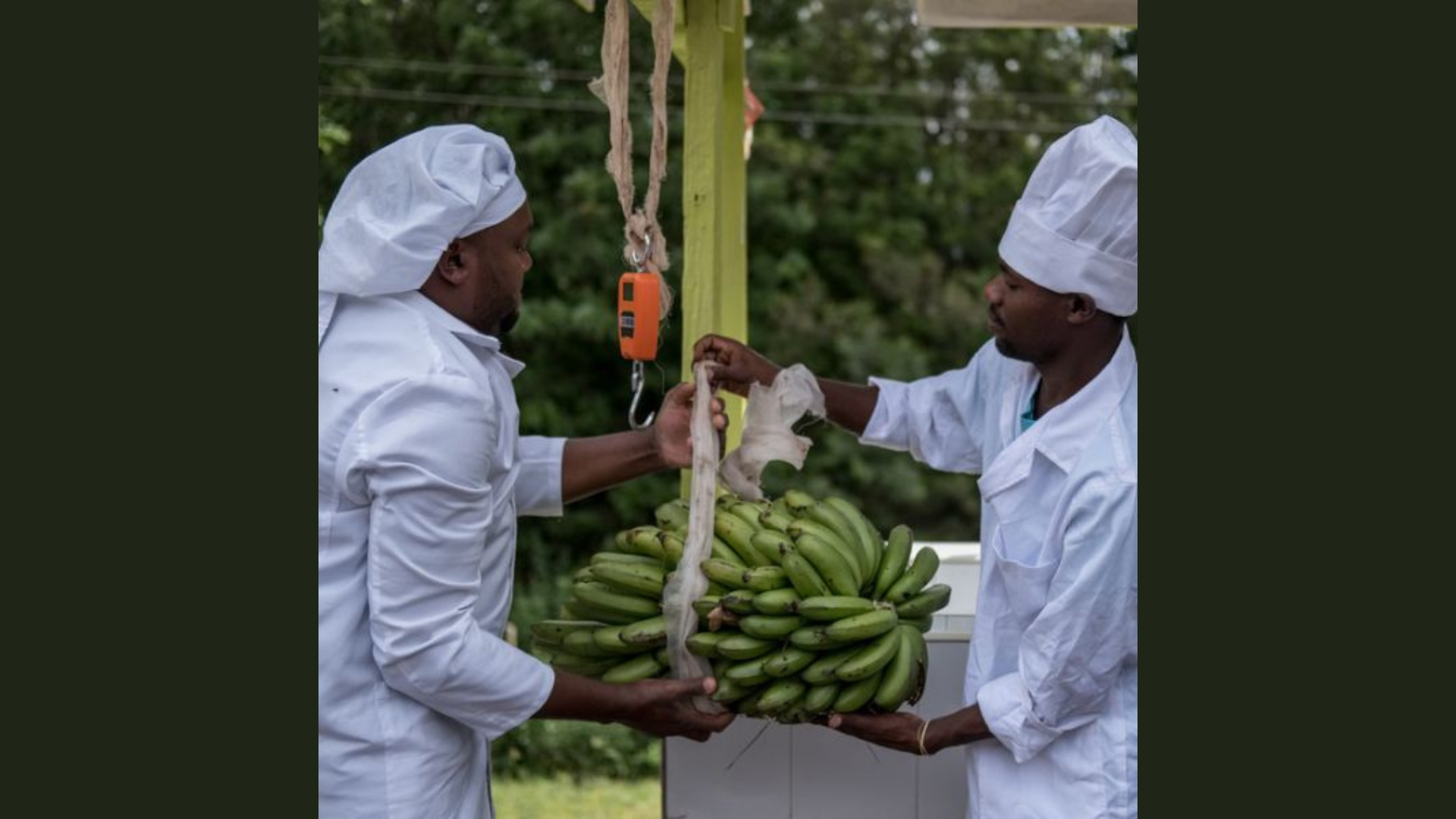
At the summit, G7 members declared their commitment to support the development of sustainable food systems in the Sahel, including local food value chains and sustainable agricultural practices. In the Sahel region, the food economy stands for more than a third (35%) of GDP in the Sahel, and the development of food systems will contribute to the structural transformation of Sahel economies and represents considerable untapped potential for the creation of decent on-farm and off-farm jobs for rural youth.
In their partnership with Sahel countries, G7 members promote a sustainable food systems approach when addressing issues of governance, planning and implementation of policies and when investing in the agri-food sector. Facilitating the involvement of young people in designing policies and furthermore promote innovation in sustainable food systems is an integral part of this concept, which includes tools to encourage youth entrepreneurship, start-ups and use of ICT as well as scale-up interventions to increase the productivity and incomes of young smallholders. G7 members intend to work with the Sahel countries to strengthen their institutions and support their strategies and policies facilitating decent job creation for youth. They will in addition collaborate through existing international initiatives and mechanisms aimed at ensuring greater donor coordination and enabling structured dialogue as well as take into account ways in which rural youth employment can contribute to addressing security and stabilisation issues in the region.
ADOPTING TERRITORIAL APPROACHES TO DEVELOPMENT
G7 members will apply their efforts in supporting and enabling governments and local authorities as well as local civil society to collaborate in designing policies that are tailored to specific territorial challenges and ensure policy coherence while acknowledging limited capacities. A strong concern will be also given to such development strategies that strengthen urban-rural linkages and encourage institutions and actors to promote active youth participation in the design and implementation of territorial development interventions and programmes.
CREATING OPPORTUNITIES AND STRENGTHENING CAPABILITIES
To create opportunities for youth the G7 expressed their will to support G5 Sahel countries in identifying challenges that impede the development of a sustainable rural economy and decent job creation. Building on this, opportunities for decent job creation can be enhanced by investing in a variety of areas including secure land tenure and equitable access to land for young people, strengthening support for family farmers, support young agriprenuers and micro small and medium enterprise development.
Regarding building capabilities, attention will also be given to national education, agricultural and rural training strategies particularly to achieve extensive scale skills development and establish training programmes that match employment opportunities and youth aspirations.
In addition, the G7 announced to support the diversification of livelihoods and promoting short term labour opportunities as well as supporting policies and practices ensuring a safe working environment. Another field to look at are nutrition services and multi-sectoral approaches that affect them. These interventions will be alongside encouraging policies and programs that create conducive conditions for young smallholder producers to gain the skills, technologies, financial and social protection instruments they need to be more competitive and earn incomes that improve their perceptions of agricultural and livestock professions.